Structural equation modelling (SEM) is one of the most popular and powerful statistical techniques for the analysis of data resulting from surveys and questionnaires, population health research, social sciences, education, psychology, business management, etc. It is highly useful in any area where numerous and mutually correlated variables are considered. The major benefit of these models is that they enable construction of networks of direct and indirect effects between the variables, thus taking into account their mutual correlations and enabling visualisation of interaction paths leading towards the dependent variable(s) of interest.
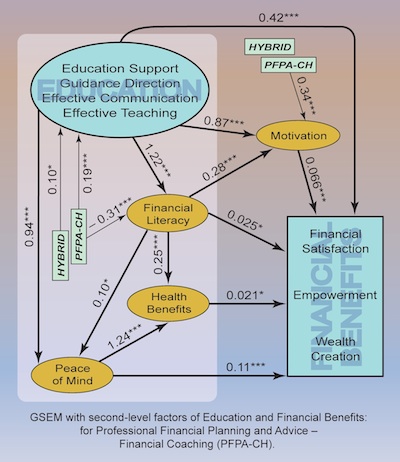 Generalised SEM (GSEM) constitutes a significant enhancement of SEM, because it enables the following additional analytical capabilities:
Generalised SEM (GSEM) constitutes a significant enhancement of SEM, because it enables the following additional analytical capabilities:
- Possibility to link a variety of different statistical models (e.g., Poisson, multinomial, etc.) into an overarching general model;
- Possibility of multi-level and mixed effects structural equation models;
- Simultaneous consideration of numerical and categorical variables in a network structure of direct and indirect effects;
- Possibility of considering categorical variables as dependent variables and enabling quantitative characterisation of probability paths towards the dependent variables.
GSEM and SEM provide unique analytical capabilities for the consideration of data problems and identification of causal direct and indirect impacts of the involved variables with much greater reliability and efficiency. They are particularly important where the multiple regression approach fails due to significant correlations between independent variables.
A structural network of effects resulting from SEM or GSEM enables accurate identification and characterisation of the most important independent variables or constructs, as well as the mechanisms and paths for their impacts on the considered dependent variables or constructs.
This opens exceptional opportunities to identify bottle-necks and issues of concern and develop strategies for the most effective (optimal) alteration of the outcomes.
SEM and GSEM are now standard and essential analytical tools for evaluation of survey and questionnaire data.

